What is predictive modeling?
Predictive modeling is a data-mining and statistical discipline that analyzes historical and current data and uses algorithms to surface trends that could affect future outcomes. It involves collecting data, formulating a statistical model, predicting, and validating (or revising) that model.
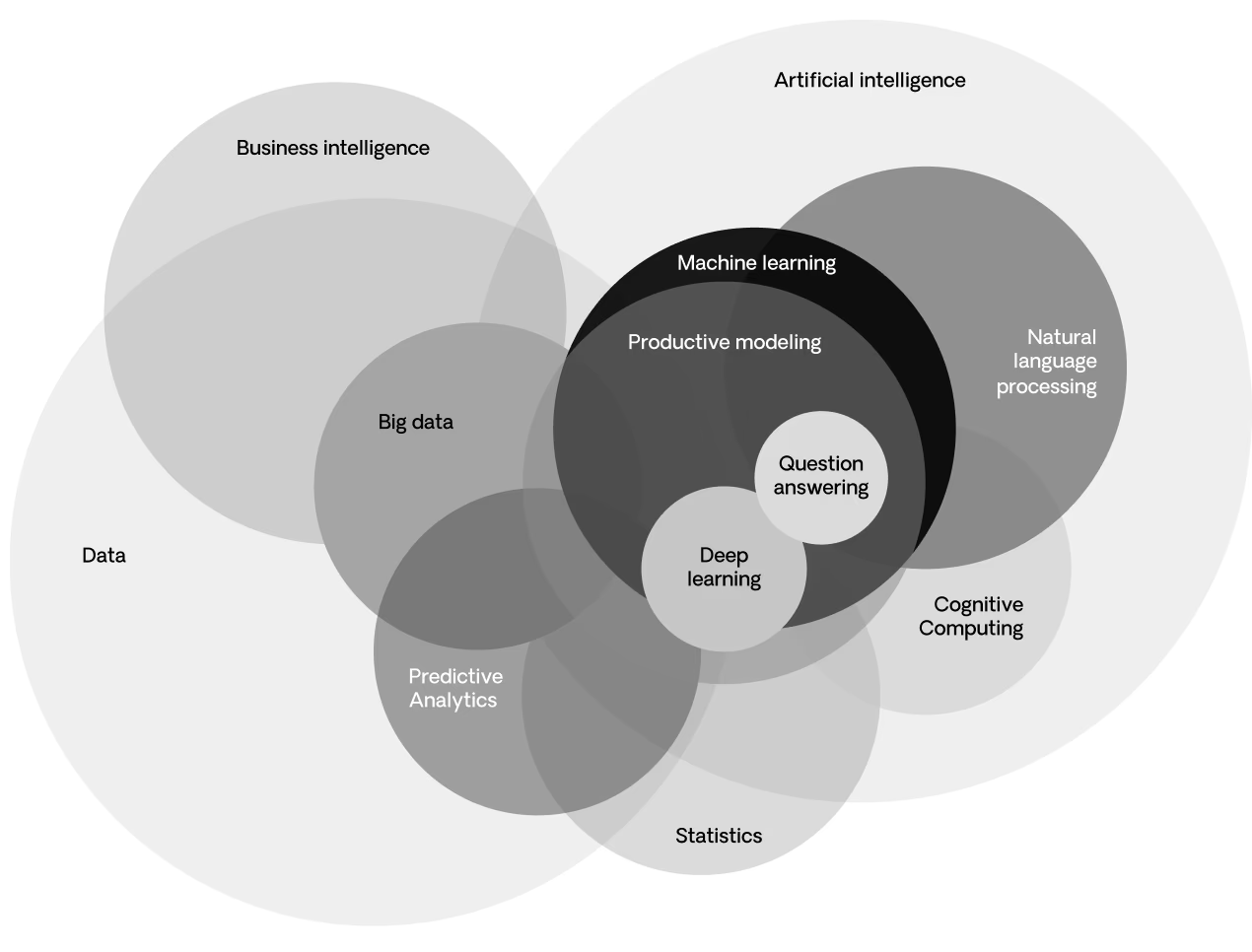
A definition of predictive modeling
Predictive modeling has been around for decades, but only recently was it considered a subset of artificial intelligence, often based on machine learning. It’s used to predict the likelihood of specific outcomes based on data collected from similar past and present events.
For example, with predictive modeling, you can calculate the probability that a customer will churn (unsubscribe or stop buying products in favor of a competitor’s). The model uses available data from customers who have churned before and from those who haven’t. This is done through patterns identified by machine learning algorithms to predict future trends.
While these predictions are commonly used for future events, they also apply to other conditions. Imagine that you want to classify the priority of a support ticket, based on its description text. After collecting data from similar tickets, you’ll be able to prioritize with an accuracy rate that’ll increase with each prediction made.
Benefits of predictive modeling
Predictive modeling is used in a multitude of scenarios, and its potential has increased now that it’s often driven by AI. But what type of benefits can you get from it?
- Predict the best outcomes: Predictive modeling's most noticeable benefit is that it can improve your decision-making process. All the relevant information about past use cases can be compiled to enhance your future choices.
- Identify hidden trends: In the past, if you had to review a high volume of data such as tickets and banking transactions or recognize and classify images manually, it was difficult to detect patterns or approve or decline events. Because of the sheer amount of data machine learning can handle, predictive modeling automatically handles events and surface trends.
- Gain operational efficiency: Along with image recognition and classification, predictive modeling can also be applied to text translation and classification. In addition, a live model's performance can be continuously improved by using the right tools and environment so that it never becomes outdated. You will also see improvement in operational efficiency and process modernization and that could lead to improved revenue and cost optimization.
Predictive modeling challenges
Amid all the AI and predictive modeling hype, a few risks tend to go unmentioned. You should bear in mind that not all data is useful, and a model may give you inaccurate predictions based on irrelevant data.
It is not always possible to predict the future of an event by its history, and correlation does not always imply causation.
When it comes to predictive modeling, there are also some ethical issues to consider. The handling of the data, its inherent bias, the algorithms, and the intellectual property rights may all come into play.
To reduce these risks, it is essential to monitor model results and compare them with reality. It is also necessary to feed the models with updated data and retrain them as their performance deteriorates. Making predictions is easy, but getting them wrong is even easier.
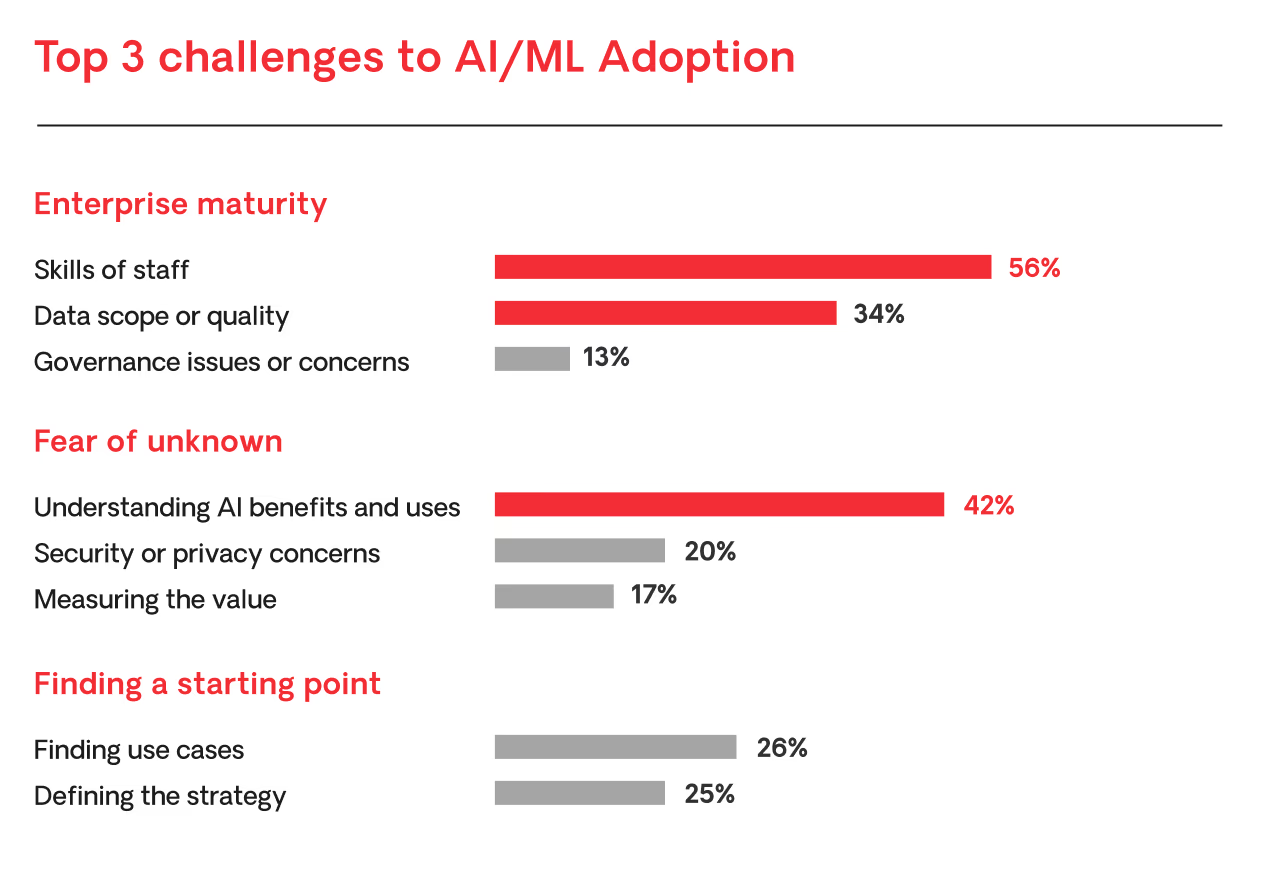
According to a Gartner report, a lack of understanding of AI is unsurprisingly one of the top three challenges in this field. To reduce the fear factor and provide a set of solid starting points for any business, let's explore a few of the most common scenarios where predictive modeling is used.
Types of predictive models
The types of predictive models vary depending on the nature of the data and the prediction task. However, some common types of predictive models include:
- Regression models: These models predict continuous numerical outcomes based on one or more predictor variables. They are used for forecasting, time-series modeling for independent and random data, and finding cause and effect between variables, Examples include linear regression, polynomial regression, and ridge regression.
- Classification models: Classification models predict outcomes by assigning observations to predefined classes or categories. Examples include logistic regression, decision trees, and support vector machines.
- Time-series models: They analyze ordered data collected over and dependent on time to forecast future values based on past observations. They are commonly used in financial forecasting, demand forecasting, and other applications where data is collected sequentially.
- Clustering models: Clustering models group similar observations into clusters or segments based on their characteristics. They are often used for customer segmentation, anomaly detection, and pattern recognition.
- Machine- learning algorithms: ML algorithms, such as random forests, gradient boosting machines, neural networks, and deep learning models, can be used for predictive modeling tasks. These algorithms can handle complex relationships and large datasets, making them versatile tools for prediction.
Examples of predictive modeling
Predictive modeling is used by a variety of businesses to manage their services and customers successfully. Here are some common examples:
Customer relationship
Future customer behavior can be proposed based on predictive modeling at any point in the journey of a product. It can, for example, be used to forecast the success of an upsell or cross-sell offer. You can improve your customer relationship processes with AI by detecting spam in public communication channels. All use cases ultimately come back to this one point of strengthening customer relationships.
Predictive modeling in marketing
Companies need to know their customers, their habits, and their behaviors in order to offer the right products. The vast amounts of data generated by clickstream flows, web, and mobile app usage, as well as many other behavioral analytics tools, make it difficult to process. In a marketing scenario, a predictive model helps by enabling the classification and segmentation of customers. When customers are assigned to cohorts, it is easier to use relevant data to detect new revenue streams and plan actions accordingly. It can also help determine the success of display advertising and predict click-through rates.
For example, a leading bank increased new account activity by 33% by targeting new movers that were relocating near bank branches and classifying them according to the likelihood of their response to a new bank account creation.
Process automation
By identifying patterns in human behavior, models can infer, with high degrees of certainty, a human decision and categorize it. This can be useful, for instance, in triage and the prioritization of cases or tickets or workforce scheduling and optimization. With swift processes, everyone can focus on more critical and non-repetitive tasks.
Automation can be further enhanced with the Internet of Things (IoT), which consists of a system of computing devices with the ability to transfer data over a network without human interaction. For example, Ricoh improved operational and cost efficiency by up to 10% by automatically scheduling repairs to minimize downtime. This was made possible by predicting when a machine is more likely to fail.
Predictive modeling in finance
Risk assessment is essential for any company, especially when making significant investments. With predictive modeling, you’ll be able to anticipate the risk of payment default or fraud, avoiding potentially critical scenarios. In the case of BBVA, it reduced the number of false positives related to fraudulent credit card transactions by 54% by predicting that risk.
Predictive modeling in insurance
A predictive model can help insurers better understand their customers. By providing more precise and detailed insights into customer risk profiles, insurers can streamline decision-making processes. This can result in enhanced efficiency and cost savings.
Predictive modeling in healthcare
When trained on vast amounts of historical patient data, predictive models can forecast patient outcomes, identify at-risk individuals, and anticipate disease progression. This proactive approach allows healthcare providers to intervene early, potentially preventing adverse events and improving patient outcomes.
These use cases are among the most common examples of how A-based predictive modeling is already making a big difference. It can now be applied to a vast number of sectors, from financial services to government, from retail to healthcare, and so many others. AI is not just the future. It’s already out there making a difference.
Take the lead with artificial intelligence
If you’re looking for a competitive advantage, machine learning and AI-based predictive modeling is the way to go. It’s more than just marketing hype, there’s real value out there, and it’s far easier to access than it was ever before.
Take a look at how OutSystems supports AI for application development
Predictive modeling frequently asked questions
The main steps for building an effective predictive model are:
- Collect data and clean it, including selecting features, dealing with missing data, and transforming data.
- Select the appropriate model and train it using the data.
- Evaluate the model and determine its accuracy.
Predictive modeling and machine learning are similar concepts for making predictions from data, but they differ in approach and scope.
- Predictive modeling uses statistical techniques to create models that make predictions based on historical data. Analysts typically define the problem, select features, and select a model.
- Machine learning is a subset of predictive modeling that focuses on creating algorithms that can learn patterns and relationships from data without being explicitly programmed.
The main difference between artificial intelligence and predictive analytics is that predictive analytics uses relational and historical data to generate output. AI, on the other hand, uses algorithms and techniques to develop systems that can learn from data independently and provide human-like intelligence.
Get up to speed on the fundamentals of artificial intelligence